
What is PTFE? Polytetrafluoroethylene, better known as PTFE, is a material founded by E.I. DuPont in 1938 and has become a widely popular choice of material when sealing a wide range of chemicals, acids, bases, and steam. This tough material cannot be compressed very easily, which is good for abrasion resistance but bad for properly sealing liquids. This is the main reason why PTFE is mostly used as a backup ring, seals, brushing, plugs, and washers.

Corrosion Resistance
PTFE is a super durable material that is highly resistive to any type of corrosion. It is pretty much unaffected by any type of chemical no matter how acidic or base heavy it is. Oils stand no chance in trying to corrode this material, and UV and sunlight have little to no accent on PTFE. This makes PTFE perfect for almost any type of installation no matter where it is used.
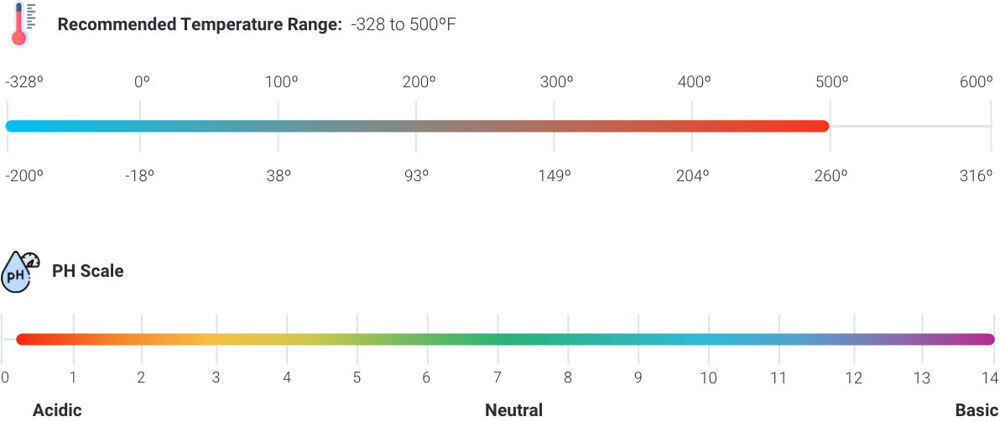
Wide Temperature Range
As seen from the chart above, PTFE has a wide range of temperature it can endure. From -328ºF to +500ºF, this material can withstand almost any extreme temperature climate it is thrown in. This material is best suited in applications such as cryogenics or high heat oven and even combustion processes.

Inelasticity & Leakage
PTFE is made from a super hard material that almost feels like plastic. The non rubber feeling material will not return to its original state if stretched or bent. PTFE O-Rings are generally not used as the main sealing material in liquid chemical applications as it could cause leakage. PTFE Backup Rings are generally used in conjunction of O-Rings. Other types of O-Rings like Nitrile, Aflas, and Fluoroelastomer are a rubber material and have elasticity with them and pair well with PTFE backup rings.









 +1 800-888-5223
+1 800-888-5223
.png)


.png)